Created by Anett Szabo, last modified by Anett Szabo 14 Aug 2007, at 05:12 PM
2.1. AOLserver
OpenACS is built atop the mighty AOLserver, the open source, multithreaded HTTP
server that powers http://www.aol.com. AOLserver provides a rich Tcl API, server-side
processing of custom tags via AOLserver Dynamic Pages (ADP), database connection
pooling and a cron-like service for running scheduled code in the background. For more
about AOLserver, please see the AOLserver home page (http://www.aolserver.com).
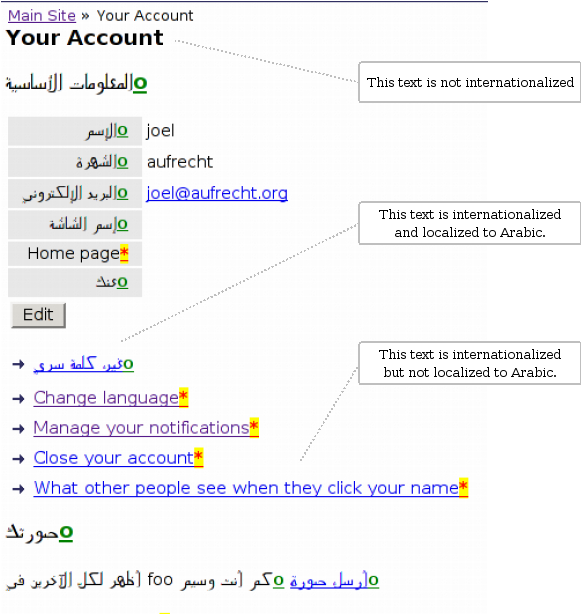
2.2. Templating system
OpenACS divides responsibility for serving most requests among two or three file types
having distinct purposes. The basic split is between a script file that sets up dynamic
variables and a markup file that renders them. The script file is a Tcl script having a .tcl
extension. The markup file has an .adp extension and looks much like standard HTML.
In fact, HTML is valid ADP, providing a gentle slope for programmers and designers
who are just getting started with the framework. Because they resemble HTML, ADP
files may be edited in standard tools such as Dreamweaver.
The OpenACS templating system supports the ability to work with page fragments via
the <include> tag. The same Tcl/ADP file pair idiom operates at this level. Hence if a
page contains a tag
<include src=”motd”>
the template system will search the current filesystem directory for motd.tcl to set up the
dynamic variables and motd.adp for the markup.
More interestingly, the OpenACS templating system supports a master/slave relationship
among page fragments. A page fragment that specifies a <master> will have its contents
embedded into the master template at a location designated by the <slave> tag in that
template. Master templates are typically used to standardize headers and footers across a
site. A nice property of the master/slave system is that the master template provides a
bird’s eye view of the entire page in a single file. And of course, the same Tcl/ADP file
pair idiom applies to master templates as well.
Before we get too far down the two-file path it’s worth pointing out a third type of file
that also participates in serving most requests: the query file. Query files have an .xql
extension and contain SQL that is specific to the template. The function of these files
will be explored further in the next section.
2.3. Database API
The OpenACS database API is designed to maximize Tcl integration with the database,
allowing data to pass back and forth as simply and naturally as possible. Let’s dive in
and consider a code example:
set title "Late Night With Conan O'Brien"
db_foreach get_matches {
select description, tvchannel, when_start, when_stop
from xmltv_programmes
where title = :title
} {
do_something_with $title $description $tvchannel
do_something_else_with $when_start $when_stop
}
This code block loops through a tv listings database looking for airings of Late Night
with Conan O’Brien. The db_foreach command runs a loop, just like Tcl’s
foreach command, but also fetches column variables for each row result, sets them in
the code block environment and finally executes the code block. Note the appearance of
:title in the SQL query, which is the second argument to db_foreach. The colon
(:) syntax serves to pass the value of the Tcl variable title to the database. This
mechanism automatically handles any quoting that may be necessary (in this case the
single quote in Conan O’Brien’s last name), an added security feature.
The first argument to db_foreach, get_matches, is a required query name. While
the above example specifices a SQL query for compactness, OpenACS scripts typically
specify their queries by name, leaving the SQL block empty. Query names are used to
look up SQL statements in special query files having an .xql extension. These sit in the
same directory next to the .tcl and .adp files, and themselves come in several flavors. For
the “motd” page fragment, standard SQL statements are places in motd.xql, Postgresspecific
statements are places in motd-postgresql.xql and Oracle-specific statements are
placed in motd-oracle.xql. This arrangement provides just enough database abstraction to
allow reuse of Tcl scripts with multiple RDBMSes, while stopping short of attempting
much larger and more difficult problems such as object-relational mapping.
The database API encompasses a number of commands that work similarly, including
db_string, db_1row, db_list, db_list_of_lists, db_multirow, etc., all
of them naturally mix with Tcl, dramatically simplifying the development of Webdatabase
applications.
The database API functions also accept an optional database name argument, to allow
applications to connect to multiple databases from the same Tcl script, if necessary.
More information: http://openacs.org/api-doc/procsearch?
query_string=db_&search_type=All+matches&name_weight=5¶m_weight=3&doc_
weight=2
2.4. Declarative programming
Among other Web development frameworks, OpenACS is still unique, powerful and
simple, and that’s based on the programming advantages created within the OpenACS,
such as declarative programming, which is understood as the opposite of writing the
logic of the program using the normal procedural programming, instead use an special
declarative syntax to reflect how the program will act, based on a possible entry, but not
relied only on that. A positive effect of writing in a declarative syntax is that the
programs usually are more robust in its behavior and more readable by other developers,
since the declarative syntax is standard and always more ordered.
2.4.1. Form processing, ad_form
As an example, for web form management, OpenACS has ad_form. This procedure
implements a high-level, declarative syntax for the generation and handling of HTML
forms. It includes special syntax for the handling of forms tied to database entries,
including the automatic generation and handling of primary keys generated from
sequences. You can declare code blocks to be executed when the form is submitted, new
data is to be added, or existing data modified.
ad_form -name form_name -export {foo {bar none}} -form {
my_table_key:key(my_table_sequence)
{value:text(textarea) {label "Enter text"}
{html {rows 4 cols 50}}}
} -select_query {
select value from my_table where my_table_key = :my_table_key
} -validate {
{value
{[string length $value] >= 3}
"\"value\" must be a string containing three or more
characters"
}
} -new_data {
db_dml do_insert "
insert into my_table
(my_table_key, value)
values
(:key, :value)"
} -edit_data {
db_dml do_update "
update my_table
set value = :value
where my_table_key = :key"
} -after_submit {
ad_returnredirect "somewhere"
ad_script_abort
}
In this example, ad_form will first check to see if my_table_key was passed to the
script. If not, the database will be called to generate a new key value from
my_table_sequence. If defined, the query defined by -select_query will be
used to fill the form elements with existing data.
On submission, the validation block checks that the user has entered at least three
characters into the textarea. If the validation check fails the value element will be
tagged with the error message, which will be displayed in the form when it is rendered. If
the validation check returns true, one of the new_data or edit_data code blocks will
be executed depending on whether or not my_table_key was defined during the initial
request. my_table_key is passed as a hidden form variable and is signed and verified.
This example illustrates how to declare a form, define validation and define a set of
actions to be taken on standard events.
More information about ad_form can be found here: http://openacs.org/api-doc/procview?
proc=ad%5fform, from which part of this sub section has been taken.
2.4.2. List builder
The list-builder is used create sophisticated table-like reports with many popular
capabilities, here is an example.
template::list::create \
-name packages \
-multirow packages \
-elements {
instance_name {
label {Service}
}
www {
label "Pages"
link_url_col url
link_html { title "Visit service pages" }
display_template {<if @packages.url@ not nil>Pages</if>}
}
admin {
label "Administration"
link_url_col admin_url
link_html { title "Service administration" }
display_template {<if @packages.admin_url@ not
nil>Administration</if>}
}
sitewide_admin {
label "Site-Wide Admin"
link_url_col sitewide_admin_url
link_html { title "Service administration" }
display_template {<if @packages.sitewide_admin_url@ not
nil>Administration</if>}
hide_p {[ad_decode $swadmin_p 1 0 1]}
}
parameters {
label "Parameters"
link_url_col param_url
link_html { title "Service parameters" }
display_template {<if @packages.param_url@ not
nil>Parameters</if>}
}
}
(taken from packages/acs-admin/lib/service-parameters.tcl)
For this example you see first the -name of the list-builder. Then the declaration of the
-multirow name used for populating the report with data, which is usually extracted
from the database. Then the -elements (columns) to be displayed in the report. Each
element is defined as a name of the variable that is set at the multirow in the case
that the variable will be used as data to be displayed in that column, like
instance_name. Also the element name can be an arbitrary name in the case that
is used the parameter display_template, which is used to include HTML tags or
ADP logic when displaying data passed by the multirow. For each element you always
define label which is the title of the column, and more special parameters such as:
link_url_col that expect a variable name which must be set at the multirow that
contains a link for automatically display the data of that column as a link.
The list builder has many more important features like order by column, filters, bulk
actions, pagination, etc.
And this is the result seen in the browser produce by the list-builder example:
2.4.3. Upgrades
Since OpenACS is a modular system consisting on independent packages, each package
has its own version and can require upgrade scripts when updating the package in a given
OpenACS installation. This is a simple example of a declarative upgrade syntax:
ad_proc -public mypackage::apm::after_upgrade {
{-from_version_name:required}
{-to_version_name:required}
} {
apm_upgrade_logic \
-from_version_name $from_version_name \
-to_version_name $to_version_name \
-spec {
2.0.3 2.1.0 {
….upgrade code here….
}
2.1.0 2.1.1 {
…. More upgrade code here….
}
}
}